Data: Data Warehouse, Lake, or Lakehouse? Which one is best for you?
Reading Time: 7 min
IDC predicts that by 2025, global data creation will reach a staggering 175 zettabytes. The digital age has ushered in an era of unprecedented data creation, leaving businesses grappling with how to harness this valuable resource best. Choosing the proper data storage solution is crucial.
Currently, three leading enterprise-grade data storage solutions dominate the market: Data Warehouses, Data Lakes, and Data Lakehouses. Each has its strengths and weaknesses and caters to specific use cases. So, how do you choose the right solution for your business?
This article delves into the pros and cons of each approach, helping you determine the ideal data storage solution for your organisation’s unique needs.
What is a Data Warehouse?
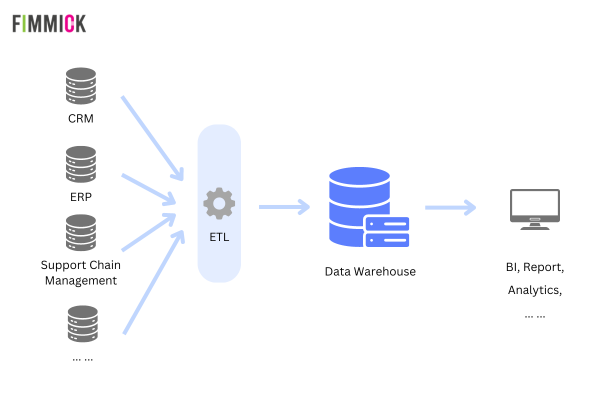
A Data Warehouse is a centralised data storage system. It utilises techniques like ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) to gather structured data from various sources, such as CRM and ERP systems. This data undergoes rigorous cleaning and transformation before being integrated into the warehouse, often in conjunction with a Customer Data Platform (CDP), ensuring standardisation and consistency.
This unified data empowers businesses to leverage Business Intelligence (BI) tools for in-depth analysis, enabling faster and more informed decision-making.
Explore Further: Customer Data Platform Guide
Advantages of a Data Warehouse
Clean, Reliable Data: Data warehouses enforce stringent data quality standards through comprehensive cleansing and transformation processes before ingestion. This ensures high data accuracy and consistency, mitigating the risk of flawed insights due to poor data quality (“garbage in, garbage out”).
Lightning-Fast Analysis: Data warehouses are built for speed. Using techniques like columnar storage, they can quickly sift through massive datasets to deliver the information you need when you need it. This means faster reporting, faster analysis, and more efficient decision-making.
Empowered Decision-Making: No more data silos or scattered spreadsheets. A data warehouse is a single source of truth, providing decision-makers with easy access to a centralised data platform. This readily available, unified view of your business empowers agile, data-driven decisions.
Challenges of a Data Warehouse
Limited Data Flexibility: Data warehouses primarily handle structured, static data. They need help to process unstructured and semi-structured data like images, videos, and social media content.
High Implementation and Maintenance Costs: The initial setup and ongoing maintenance of data warehouses can be expensive, potentially posing a barrier for smaller businesses.
What is a Data Lake?
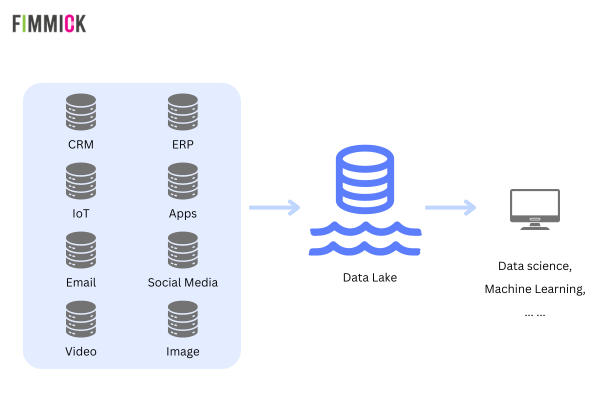
A Data Lake is a centralised repository designed to store vast amounts of raw data in its native format, encompassing structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data types. This inherent flexibility sets it apart from other data storage solutions. Unlike Data Warehouses, which employ a “schema-on-write” approach, Data Lakes utilise a “schema-on-read” model. This means data is stored in its raw form and only structured or transformed when accessed and ready for use.
Explore Further: What is CRM, DMP and CDP?
Advantages of a Data Lake
Powerful Data Integration: Data Lakes break down data silos by providing a single repository for data from diverse sources, simplifying data management and fostering a unified view of your data landscape.
Unparalleled Flexibility: The “schema-on-read” approach allows users to store data in its raw format. It provides the flexibility to structure and transform data on demand, adapting to evolving business needs and analytical requirements.
Cost-Effective Storage: Data Lakes offer highly scalable storage at a fraction of the cost of traditional enterprise data warehouses. The cost per terabyte of data stored annually can be significantly lower, making it a budget-friendly solution for managing massive data volumes.
Enables Advanced Analytics and Machine Learning: Data Lakes are rich data sources for data scientists and machine learning engineers, providing the raw material to fuel data mining, machine learning, and artificial intelligence applications.
Explore Further: What is Data Activation?
Challenges of a Data Lake
Data Governance: The variety of data stored in a Data Lake can lead to consistency in data quality. Without robust data governance frameworks and processes, Data Lakes risk becoming “data swamps” – replete with unreliable, inaccurate data that undermines analysis and decision-making.
Query Performance: Since Data Lakes store raw, unprocessed data, complex queries can lead to performance bottlenecks. Unlike optimised Data Warehouses, querying a Data Lake requires scanning massive amounts of data, resulting in slower query responses.
Explore Further: What is Dark Data?
What is a Data Lakehouse?
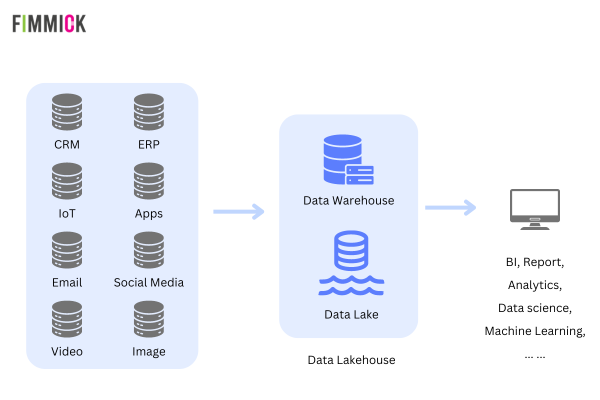
A Data Lakehouse represents a modern evolution in data management, seamlessly blending the best of both Data Warehouses and Data Lakes. This hybrid approach combines the robust data management and analytical capabilities of a Data Warehouse with the flexibility and cost-effectiveness of a Data Lake.
Advantages of a Data Lakehouse
Reduced Data Redundancy: Traditional data architectures often require replicating and moving data between Data Lakes and Data Warehouses to support various use cases, leading to wasted storage and increased complexity. Data Lakehouses eliminates this redundancy by supporting diverse data formats and analytical workloads within a unified platform. For example, after adopting a Lakehouse architecture, Airbnb reported significantly reduced computing resources (over 50%) and job runtimes (40%).
Cost Optimisation: Data Lakehouses leverage cost-effective cloud storage solutions and tiered storage management techniques, minimising storage and data movement costs. This results in significant cost savings compared to maintaining separate Data Lake and Data Warehouse environments.
Broader Range of Data Applications: Data Lakehouses cater to a broad spectrum of data-driven initiatives, seamlessly supporting data analytics, business intelligence, machine learning, and artificial intelligence workloads within a single, unified environment.
Enhanced Data Management and Security: Data Lakehouses typically incorporate robust data governance features like version control, lineage tracking, and access control. These capabilities ensure data traceability, accountability, and security, enabling organisations to manage and protect their valuable data assets confidently.
Challenges of a Data Lakehouse
Relatively New Technology: As a relatively nascent technology, Data Lakehouses are still maturing in areas like performance optimisation, long-term stability, and ecosystem maturity. Organisations should carefully evaluate these aspects and consider potential limitations before fully committing to a Data Lakehouse architecture.
Choosing the Right Data Storage Solution for Your Business
Selecting the optimal data storage solution is not about identifying the single “best” option. Instead, it requires carefully evaluating your organisation’s specific business needs, technical capabilities, and budget constraints.
Here are some key factors to consider:
Data Type and Volume:
Data Warehouse: Well-suited for structured data and more minor to medium-sized datasets, offering robust analytical capabilities.
Data Lake or Data Lakehouse: These are ideal for handling large volumes of unstructured data, providing flexibility and scalability for evolving data needs.
Data Application Scenarios:
Data Warehouse: Excels in supporting complex data analysis, reporting, and business intelligence applications requiring high query performance.
Data Lake: A robust foundation for data science, machine learning, and AI applications, providing access to vast amounts of raw data for exploration and model training.
Cost Considerations:
Data Warehouse: Typically involves higher upfront investment and ongoing maintenance costs, particularly for scaling data storage and processing.
Data Lake and Data Lakehouse: Offer lower storage costs, especially with cloud-based solutions. However, operational expenses can increase based on the complexity of data processing and analysis required.
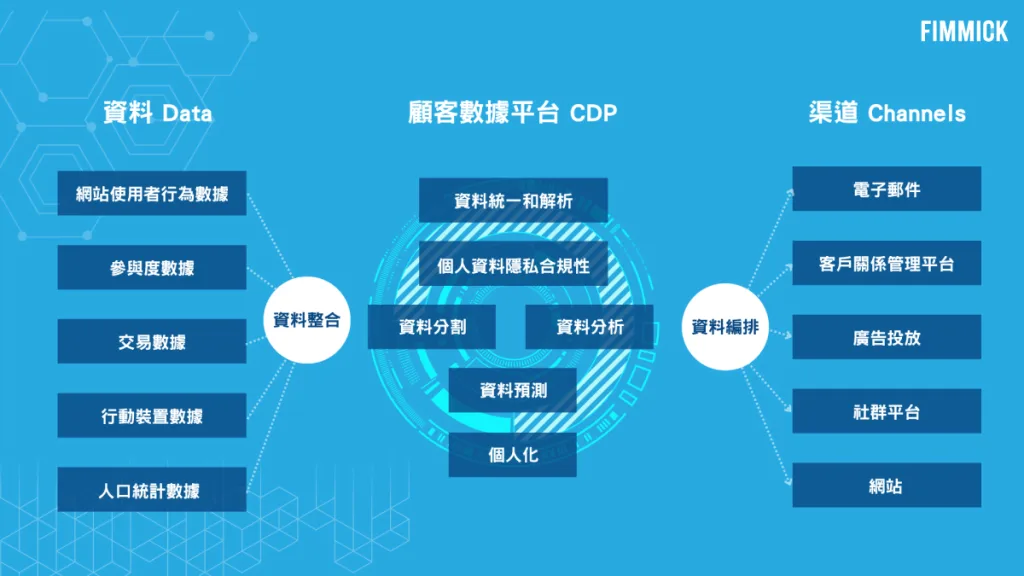
Unify Your Customer Data with FIMMICK CDP
- Build a Single Source of Truth: Eliminate data silos and create a centralised repository of first-party customer data.
- Create a 360-degree Customer View: Unified data allows you to gain a holistic understanding of your customers, enabling personalised experiences and targeted campaigns.
- Unlock Data-Driven Insights: Extract actionable insights from your customer data to inform marketing decisions, optimise ad spend, and drive business growth.
- Automate Customer Journeys: Improve operational efficiency and deliver personalised customer experiences through automated lifecycle marketing campaigns.
- Reduce Churn: Proactively identify at-risk customers and implement targeted retention strategies based on real-time behavioural insights.
- Ensure Data Security and Compliance: Manage and protect your valuable customer data with robust security measures and adherence to data privacy regulations.
Conclusion
Data Warehouses, Data Lakes, and Data Lakehouses offer distinct advantages for managing and leveraging data. Choosing the right solution depends on your organisation’s specific data characteristics, use cases, budget, and long-term data strategy. By carefully evaluating these factors, businesses can select the optimal approach to unlock the full potential of their data assets.
Related Solutions
Related Articles

CRM: How to Choose a CRM system – Tips & Considerations
Unlock the power of CRM with this comprehensive guide to choosing the right system. Learn about the different types of CRM, key features.

CRM: Unlocking The Power of Customer Lifecycle Management
In this article, we’ll explore Customer Lifecycle Management (CLM) strategies to transform one-time purchases into lasting customer loyalty and brand advocacy.

Ecommerce: 6 Critical Things Ecommerce Startups Often Miss
Launching an online business is exciting, but many startups stumble over critical early steps. Let’s explore the 6 items startups often miss.









